The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is set to transform the UK insurance industry, particularly in areas like claims processing and underwriting, Tony Van Niekerk, COVER

As AI technology evolves, insurers must recognise its potential to streamline processes, enhance decision-making, and improve customer experiences. However, careful planning is required to address potential technical, cultural, regulatory, and ethical challenges. A survey conducted by The Insurance Network (TIN) and Sapiens in August and September 2023 explored these opportunities and obstacles, capturing insights from senior executives in IT, claims, underwriting, and data management across the general insurance and London markets.
Understanding AI and Its Role in Insurance
The survey begins by differentiating traditional AI and generative AI. Traditional AI, or Narrow AI, specialises in specific tasks within a defined framework, such as voice assistants or recommendation engines. It works within set algorithms and predefined rules to make informed decisions. Generative AI, on the other hand, marks a leap forward by using patterns from large datasets to generate new content, making it a transformative force in the insurance industry. This advanced form of AI can reshape the entire insurance value chain, impacting everything from product development to risk assessment, fraud detection, and customer engagement.
Key Opportunities Identified
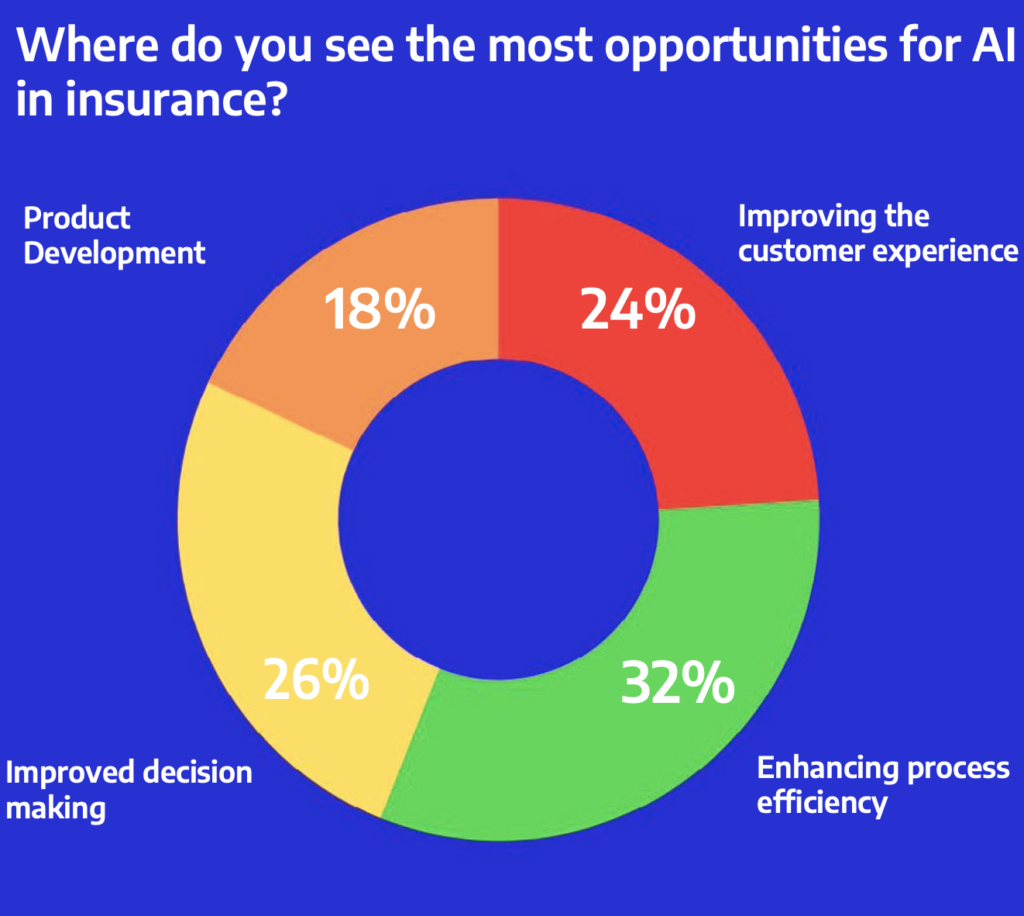
The survey asked participants to identify the most significant opportunities for AI in insurance:
- Process Efficiency: The most prominent opportunity is enhancing efficiency across the product lifecycle. AI can standardise and automate processes like document and data retrieval, significantly reducing manual input. For instance, AI’s ability to extract and analyse data enables automated decision-making, provided the data’s accuracy is high.
- Improved Decision-Making: AI also offers support in data analysis, enhancing insurers’ ability to validate models and make better-informed decisions. Participants emphasised how AI’s ability to classify and summarize large volumes of data is crucial for intelligent decision-making.
- Customer Experience: AI can enhance customer service through self-service options, such as chatbots, reducing human touchpoints while providing timely support. Although this was not the highest-ranked opportunity, it demonstrates AI’s potential to revolutionise customer interactions.
- Product Development: Although this ranked fourth, respondents acknowledged AI’s role in driving innovation by analysing large datasets to develop new insurance products.
AI’s Impact Areas in Insurance
Participants were also asked which areas AI impacts or will impact most significantly. They ranked the following:
- Document Interrogation: Respondents highlighted AI’s ability to process large, complex legal contracts and claims files quickly, enhancing efficiency in document handling. This capability is particularly valuable in the London market, where rapid document analysis supports better client outcomes.
- Pricing & Underwriting: AI’s capacity for predictive accuracy and automation is seen as critical in underwriting. By analysing vast datasets (e.g., property details, historical claims, weather data), AI can create detailed risk profiles, aiding in precise underwriting and personalized policy pricing.
- Claims Processing: AI’s applications in claims processing include automating queries and payments, pattern recognition for fraud detection, and optimizing settlement recommendations. These capabilities enhance efficiency, resulting in quicker resolutions and improved customer satisfaction.

Navigating fraud challenges together
Connect, visualise and analyse data to identify and stop fraud with DataWalk: Our graph analytics platform using AI & ML to solve fraud challenges.
Current and Future Use Cases for AI
The survey revealed that 52% of respondents already have AI use cases in their organisations. Examples include:
- Analytics for Pricing & Underwriting: AI is used to improve data analytics and pricing strategies.
- Broker Efficiency: AI enhances the efficiency of broker interactions by streamlining processes.
- Document Ingestion: Automating document handling reduces manual labor and boosts efficiency.
- Data Validation: AI supports the transition from Word-based to digital policies, ensuring accuracy in policy management.
- Customer Interaction: AI enhances customer engagement through automation in voice and online channels.
Future potential use cases cited by respondents include:
- Claims Automation: Automating straightforward claims and categorizing complex ones using AI models.
- Advanced Pricing Models: Personalised pricing models and competitor analysis through automated data gathering.
- Enhanced Document Interrogation: Using natural language processing for compliance checks and policy verification.
- Marketing & Communications: Personalized customer communications and real-time sentiment analysis using AI-driven tools.
- Onboarding: Automating data extraction and centralising documentation for faster onboarding processes.
AI’s Implications for Insurance Operations
Respondents were asked to evaluate statements on AI’s impact on insurance operations:
- Efficiency and Job Roles: Most agreed that AI would enhance efficiency, potentially reducing headcount but also transforming job roles. AI is expected to shift work away from repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities like customer service and strategic decision-making.
- Bias and Decision-Making: A consensus emerged that AI could reduce data entry errors and improve decision-making accuracy. However, concerns about AI-induced biases remain, emphasising the need for robust monitoring and governance to ensure compliance with ethical standards.
- Regulation and Automation: Respondents advocated for a hybrid approach, where AI systems recommend actions that humans review, maintaining accountability and transparency in decision-making.
Challenges in AI Implementation
The survey identified several obstacles to AI adoption:
- Data Quality: Ensuring high-quality data is critical for successful AI deployment. Inaccuracies in data could undermine trust in AI systems.
- Skills and Capabilities: Attracting and retaining skilled professionals is essential for leveraging AI’s potential.
- Data Accessibility: A robust data infrastructure is necessary for AI-driven decision-making.
- Budget Constraints: Financial and stakeholder buy-in challenges persist in AI implementation.
- Legacy Technology and Regulation: Outdated systems and regulatory compliance complexities add layers of difficulty to AI adoption.
Despite these challenges, respondents remain optimistic. Many highlighted the importance of step-by-step integration and a measured approach to building trust and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
The survey underscores AI’s transformative potential in the UK insurance industry. While it offers numerous opportunities to enhance efficiency, decision-making, and customer experiences, careful attention must be paid to ethical, regulatory, and operational challenges. As insurers continue integrating AI, a balanced approach that combines technology with human oversight will be essential to maximise benefits while minimizing risks.
By addressing these obstacles strategically and thoughtfully, insurers can position themselves to harness AI’s capabilities, ensuring competitiveness and resilience in an evolving marketplace.

