By: Digital Platform Quotes Advisor
The country is responsible for approximately 40% of all sector revenue in Africa.
The rise of digital wallets has revolutionised the way we conduct financial transactions, offering a range of significant benefits as a payment method. Convenience, security, and accessibility are just some of the advantages these platforms offer users, allowing them to make transfers quickly and in an efficient way.
As highlighted by the World Bank, financial inclusion is a key factor for countries’ economic development and stability, as well as for achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
These innovative technologies are not only democratising access to financial services but also strengthening the economic infrastructure, as seen in South Africa, where it is rapidly gaining ground.
In fact, South Africa’s fintech landscape is constantly evolving, and significant changes are expected in 2024 driven by regulatory changes, technological improvements, and increasing competition.
Fintech encompasses a wide range of products and services, from online banking to mobile payments, peer-to-peer lending, digital wallets, and financial management tools.
According to a report published by Research and Markets, the country has been internationally recognised for having one of the most sophisticated financial sectors, generating approximately 40% of all fintech revenue in Africa.
Over the past decade, this recognition has been reinforced by a growing sector which, although small, is experiencing rapid development and transforming the financial sphere through digitisation, streamlining, and in some cases, disruption.
In this context, Dawid de Villiers, Gabi Richards-Smith, and Lerato Lamola, fintech experts from Webber Wentzel, have anticipated that 2024 will bring significant advances in South Africa’s fintech industry.
Among the five key predictions are guidelines for generative artificial intelligence and machine learning, payment laws modification, changes in cryptocurrencies and blockchain, an open finance framework, and an increase of participants in mobile banking and financial services.
Specifically, specialists expect for the implementation of the planned amendments to the National Payment System Act, which covers the management, administration, operation, regulation, and supervision of payment, clearing, and settlement systems. “We expect to see amendments that encourage greater participation of non-bank actors in the payment system”, stated the expert sources.
Likewise, the conclusion of the Conduct of Financial Institutions Bill is anticipated, which could include provisions related to activities linked to payment systems. These initiatives reflect an effort to promote inclusion and efficiency in the South African financial landscape.
In the same line, an increase in the number of financial service providers using mobile telecommunications services is also expected in the sector. To this end, it is expected that more foreign investments will enter the South African market, both in local companies and participants from other regions.
In 2023, the use of digital payments in South Africa experienced rapid growth, surpassing even the expansion of e-commerce. Digital wallets and contactless payment systems, such as Apple Pay, Samsung Pay, and Google Pay, gained significant momentum among consumers.
A recent study by Stitch, a payments infrastructure company, revealed that over 50% of surveyed South Africans choose to use digital wallets and contactless payment systems when making purchases in commercial establishments.
It is noteworthy that the survey, conducted in collaboration with the research firm Yazi, collected data from over 350 people in December of last year, providing insight into emerging trends in the country’s digital operations environment.
According to the findings, South Africans allocate approximately 10% of their income to online purchases. The increase in online spending has favored the use of cards, which remain the predominant method in e-commerce.
However, market growth and demand for more efficient payment options have led to the emergence of new alternatives, such as bank transfers and, increasingly, digital wallets and contactless systems, which compete with cards in both online transactions and physical stores.
“Compared to a similar study conducted in December 2022, this year’s survey found a very different picture (…) even if card and bank payment remain the top preferences, chosen by 71.8% and 43.9% of respondents, respectively, as at least one of their preferred options, additional touch payment methods such as Capitec Pay and even mobile money have gained ground,” the report indicates.
The case of Capitec Pay, mentioned by 25.9% of respondents despite its launch just last year, demonstrated that South Africans are willing to adopt new options that fit their constantly evolving needs.
“This creates an opportunity for attractive options to enter the market and better address customer needs. For companies, one way to manage and optimize new and multiple payment providers and methods is through payment orchestration platforms, which allow them to easily view and reconcile all transactions between methods in one place and optimise based on which one performs the best,” the study adds.
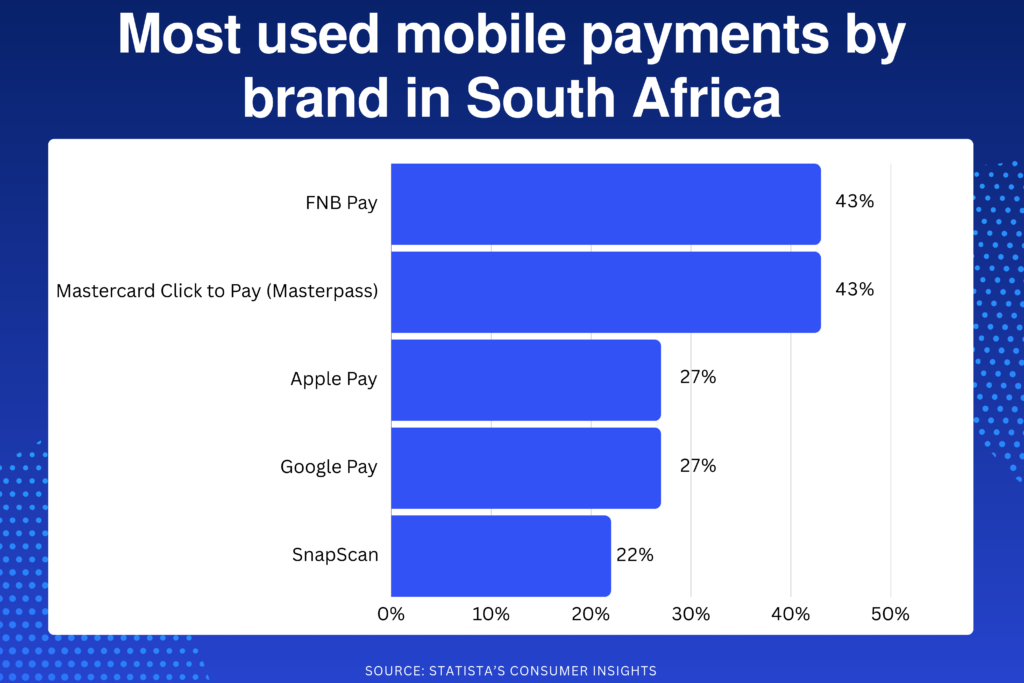
Meanwhile, a survey conducted by Statista’s Consumer Insights showed the most used mobile payments by brand last year, with FNB Pay and Mastercard Click to Pay taking the top spot with 43%, followed by Apple Pay (27%), Google Pay (27%), and SnapScan (22%) closing the top 5.
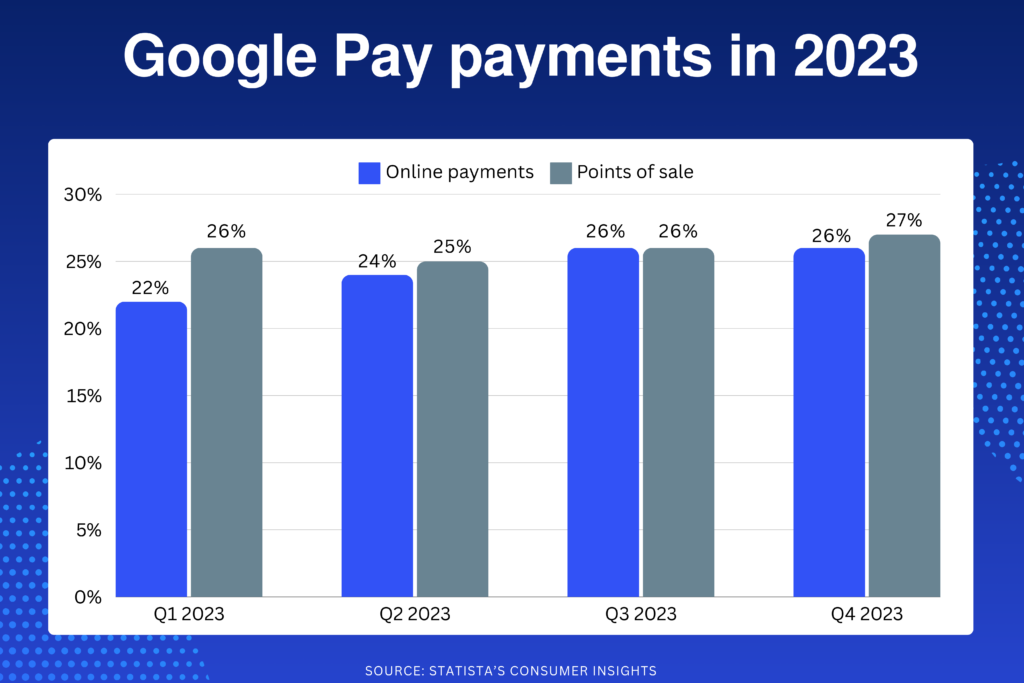
Another Statista research on the adoption of Google Pay for online transactions in South Africa showed a decrease in 2023 compared to early 2020, although usage among consumers remained relatively constant.
The figures presented reflect the percentage of respondents who reported having used the application in the last 12 months, either for point-of-sale transactions with a mobile device in stores and restaurants, or for online purchases.
I also showed that, during the period from April 2022 to March 2023, 2 out of every 10 respondents indicated having used Google Pay at a point of sale, while another 2 out of 10 said they used it for online payments during the same period.
Contactless Payment Scams
Contactless payment methods, including the use of cards, smartphones, or smartwatches, have experienced a notable increase in popularity. However, this technological convenience has also been used by scammers.
According to the Ombudsman for Banking Services, Reana Steyn, fraud through digital wallets is on the rise, and criminals are linking stolen card information with their smart devices.
In this regard, the representative warned about a new modality that involves the use of Near Field Communication (NFC) technology. In this practice, scammers use stolen card data to make fraudulent purchases through digital wallets.
Moreover, in most cases, digital purchases do not require a unique PIN (OTP) to complete a transaction, facilitating the crime. “Unlike normal fraudulent card-not-present (CNP) transactions we are used to, where scammers would use stolen card information to make online purchases, and which would cause OTPs to be sent to the legitimate cardholder’s registered cellphone number for each transaction made, NFC payments/digital wallet do not require this additional OTP mitigation tool for each and every transaction,” said Steyn.
In line with the above, the spokesperson indicated that, in a short period, they received 120 complaints related to NFC frauds, which are currently under investigation. Losses linked to these incidents represent millions of rands, especially in fraudulent purchases made in nations such as the United Arab Emirates, France, and Spain.
“This clearly demonstrates the presence of an international criminal syndicate operating in this area and targeting South African consumers,” Steyn affirmed. Additionally, he confirmed that one of the country’s major banks recorded over 6,000 complaints between January 2022 and June 1, 2023. He expressed concern in this regard, as the considerable losses incurred have the potential to create serious financial difficulties for bank customers, some of which could be insurmountable in certain cases.
Thus, while the use of contactless payment methods has brought numerous advantages, facilitating quick and secure transactions in various situations, it is crucial to recognise that this convenience carries risks, as criminals can exploit these technologies to commit fraud and generate significant losses for both individuals and financial institutions.


